Product Profile
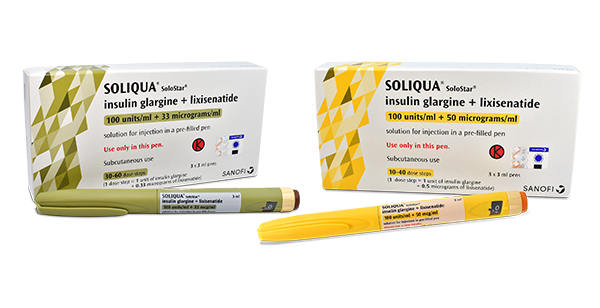
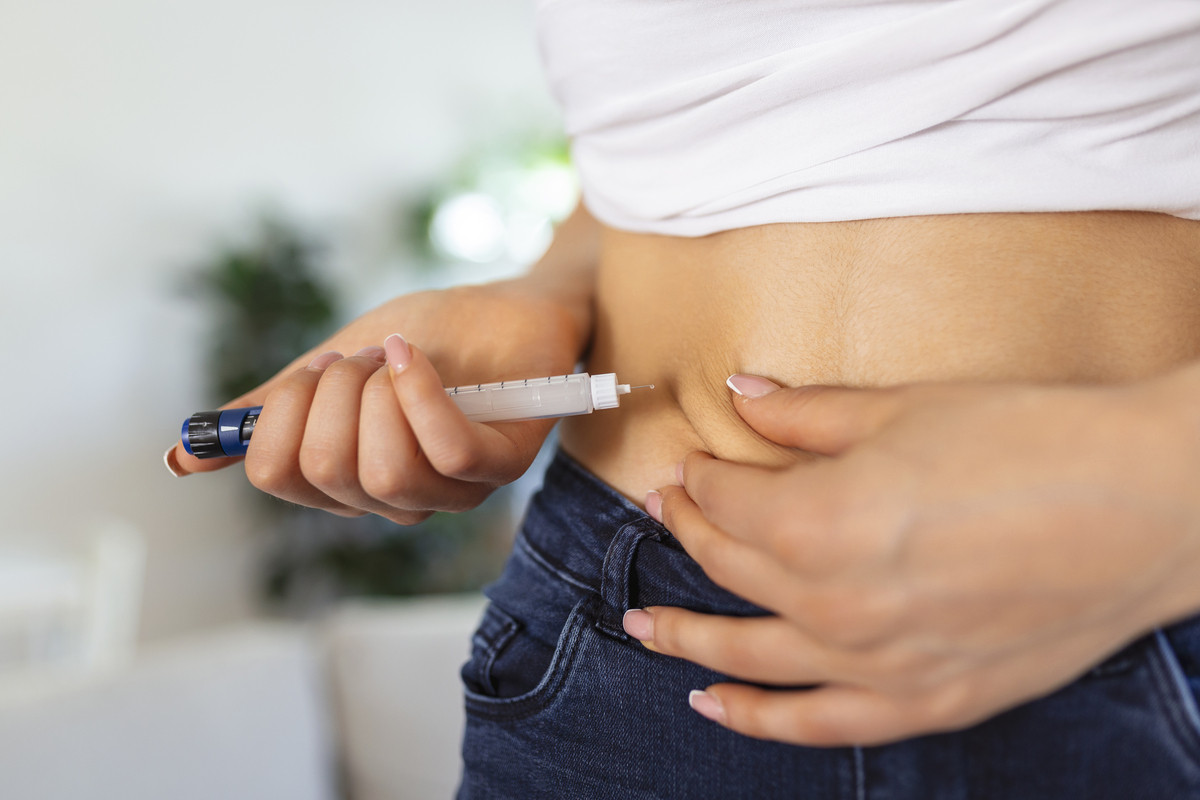
SOLIQUA
BRANDED
Soliqua 100 units/mL + 50 microgram/mL solution for injection in a prefilled pen, Soliqua 100 units/mL + 33 microgram/mL solution for injection in a prefilled pen
Related Articles