HbA1c levels are currently considered the gold standard for monitoring the effectiveness of therapy in patients with diabetes in daily clinical practice and even in clinical trials. However, the interpretation of HbA1c levels should still be done carefully and would be better if supported by other supporting data such as self-monitoring of blood glucose with capillary blood samples or more modern modalities such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM).1
There may be significant discrepancies between HbA1c levels and average glucose levels due to fluctuations in blood glucose levels. Recent innovations such as CGM can be a solution to this problem. Recent evidence shows that the percentage of time above range (%TAR) and the percentage of time in range (%TIR) obtained using CGM have a higher correlation with average glucose when compared to HbA1c levels and can be a more specific indicator for assessing the efficacy of therapy.1 Various studies also show that the use of CGM can help improve glycemic control in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.2
Accurate monitoring to describe the state of glycemic control is very important as a guide for initiating therapy intensification, as well as preventing therapeutic inertia. The phenomenon of therapy inertia itself is a major cause of suboptimal glycemic control. To achieve glycemic control targets, it is very important to intensify therapy in a timely manner. Data shows that therapy intensification is often done too late with a median time of around 2.9 years. Delayed intensification has a significant impact on patient outcomes, where a delay of one year is correlated with an increased risk of heart attack by 67%, heart failure by 64% and stroke by 51%.2
The selection of the right therapeutic modality for therapy intensification and also supplemented by the use of CGM to guide decision-making accurately has the potential to reduce the occurrence of therapy inertia.2 One innovative modality that can be considered for therapy intensification in patients with diabetes is the combination of basal insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), such as IGlarLixi (insulin Glargine + Lixisenatide). Timely therapy intensification with IGlarLixi can help improve the achievement of TIR compared to using basal insulin alone or GLP-1RA alone and does not increase the risk of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.3
The results of the Soli-D study4 published in 2024 show evidence that once-daily IGlarLixi injection can provide effective all-day glycemic control. In addition, patients who received IGlarLixi were correlated with lower self-monitored blood glucose values (checked 7 times a day) compared to patients who received IDegAsp (insulin Degludec + Aspart co-formulation) after 24 weeks.4
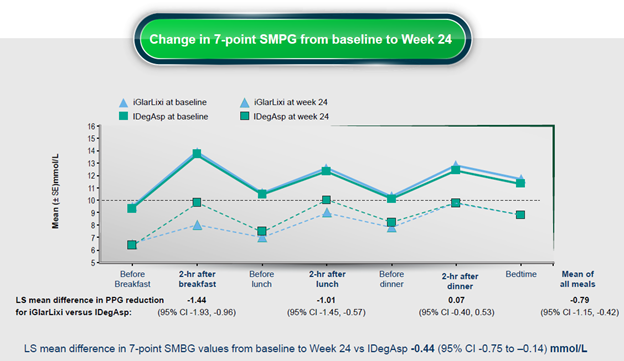
Figure 1. Changes in self-monitored blood glucose values after 24 weeks in patients receiving IGlarLixi compared to IDegAsp. Note: SMPG: self-monitored plasma glucose; LS: least significance; CI: confidence interval; PPG: post-prandial glucose. (Figure adapted fromLiu M, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024)
In addition, recent data also show the benefits of IGlarLixi administration for improving glycemic control based on CGM examination. Results from the Soli-CGM study showed that IGlarLixi therapy intensification in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (HbA1c ≥ 9%) with at least 2 can increase the percentage of TIR from 26.4% at the beginning of the study to 52.7% after 16 weeks (average change 26.2%, 95% CI: 20.5%-31.9%; p <0.001).5
Conclusion
The use of CGM and timely therapy intensification with IGlarLixi can be considered as one strategy to improve the achievement of glycemic control in patients with poorly controlled diabetes without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. Recent data show that once-daily administration of IGlarLixi can control blood sugar throughout the day, and can improve glycemic control as indicated by an increase in TIR values obtained from CGM examination.
Image: Illustration (downloaded from https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/high-angle-diabetic-woman-checking-her-glucose-level_65609387.htm#fromView=search&page=1&position=34&uuid=2dcae00d-3d14-4a23-b368-34b24ced3e64, Image by Freepik)
References:
1. Rodbard D. Continuous glucose monitoring metrics (Mean Glucose, time above range and time in range) are superior to glycated haemoglobin for assessment of therapeutic efficacy. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(2):596-601. doi: 10.1111/dom.14906.
2. Martens TW and Parkin CG. How use of continuous glucose monitoring can address therapeutic inertia in primary care. Postgrad Med. 2022;134(6):576-588. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2080419.
3. Guo X, Yang W, Zhang J, Dong X, Liu M, Gu S, et al. iGlarLixi provides a higher derived time-in-range versus insulin glargine 100 U/mL or lixisenatide in Asian Pacific people with type 2 diabetes: A post hoc analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(7):2005-2011. doi: 10.1111/dom.15074.
4. Liu M, Gu W, Chen L, Li Y, Kuang H, Du Jet al. The efficacy and safety of iGlarLixi versus IDegAsp in Chinese people with type 2 diabetes suboptimally controlled with oral antidiabetic drugs: The Soli-D randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(9):3791-3800. doi: 10.1111/dom.
5. Frias JP, Dex T, Meneghini L, Amelie R, Shah V. Effect of IGlarLixi on continuous glucose monitoring-measured time in range in insulin-naïve adults with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes (A1C ≥11.7–18.1 mmol/L/9–13%) Presented at ATTD 2024. Oral Presentation #02