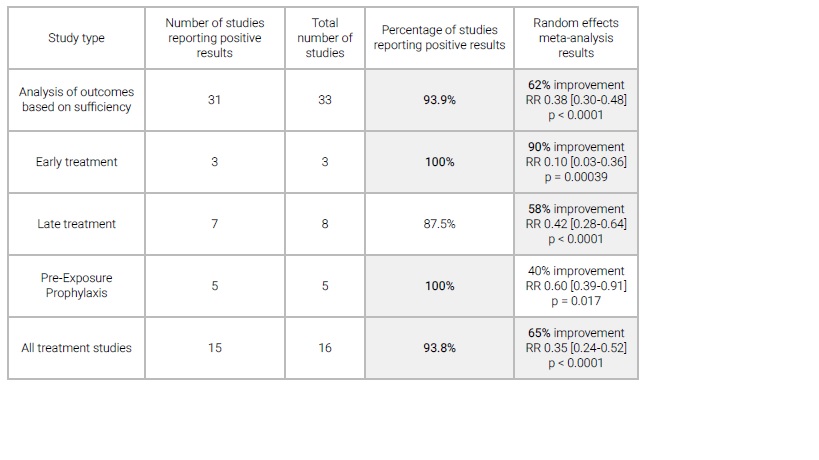
The results of the meta-analysis (a total of 49 studies) showed that vitamin D was effective for Covid-19 patients. Adequate vitamin D levels were associated with a 62% reduction in risk (infection, hospitalization, progression, and death) (from 33 studies), and vitamin D therapy (from 16 studies) was associated with a reduced risk (progression, death) by 65%.
Vitamin D has been identified in relation to bone health, and currently known vitamin D have many other functions, including a vital role in the immune system.
An analysis of 49 significant studies related to vitamin D and Covid-19 (n = 16,392) was conducted to analyze outcomes based on adequacy of vitamin D levels, mortality, and study of therapy in each stage of therapy. In general, low vitamin D levels are associated with many factors that can affect susceptibility to Covid-19 and the severity of Covid-19. Studies also show a link between adequate vitamin D levels and outcomes.
Note:
Early treatment: therapy as soon as symptoms appear
Late treatment: slower therapy
Pre-exposure prophylaxis: take vitamin D regularly before getting infected
A meta-analysis of 33 studies showed that adequate vitamin D levels were associated with a 62% reduction in risk (infection, hospitalization, progression, and death) (RR 0.38; 95% CI 0.30–0.48).
Meta-analysis from studies on vitamin D therapy even now resulted in a 65% reduction in risk (progression, mortality) (RR 0.35; 95% CI 0.24-0.52).
From this study concluded that vitamin D was effective for Covid-19 patients.
Image: Ilustration (www.pexels.com)
Reference:
Vitamin D is effective for COVID-19: real-time meta analysis of 49 studies. Covid Analysis, Dec 17, 2020 (Version 24, Feb 17, 2021) [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2021 Feb 18]. Available from: https://vdmeta.com/